Browse Eyewear

Are you looking for effective ways to slow down the progression of this eye disease and protect your vision? Look no further! In this blog post, we have curated 9 valuable tips that can help prevent the advancement of this condition. From lifestyle changes to medication management, our expert advice is sure to give you the tools necessary for a healthier future. Read on and discover how easy it can be to take control of your eye health and stop glaucoma in its tracks!
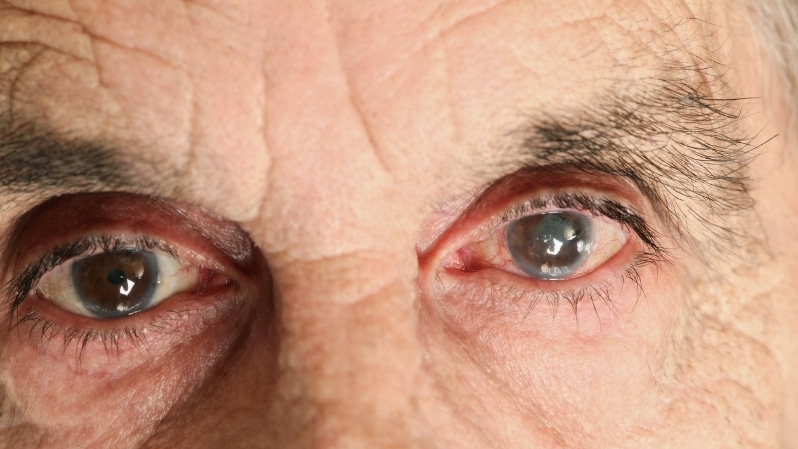
Signs and Symptoms of Glaucoma
The most common sign of early glaucoma is elevated intraocular pressure or IOP. However, this alone does not necessarily mean you have glaucoma. You may also experience:
• Eye pain
• Headache
• Nausea and vomiting
• Severe eye redness
• Tears in the front of the eye
As glaucoma progresses, you may start to experience tunnel vision and your field of vision may narrow. In its late stages, glaucoma can cause blindness.
Tips to Stop the Progression of Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness if left untreated. There are many different ways to treat glaucoma, but the most important thing is to catch it early and prevent it from progressing. Here are 9 tips for stopping the progression of glaucoma:
Regular Eye Examinations
It is important to have regular eye examinations to check for changes in your vision and the health of your eyes. Your doctor will be able to tell if you are at risk for glaucoma and can prescribe treatment to help slow or stop the progression of the disease.
Proper Nutrition
A comprehensive guide to glaucoma would not be complete without a discussion of nutrition and how it can impact the disease. Proper nutrition is important for general eye health and can also help slow the progression of glaucoma.
There are a few key nutrients that are especially important for people with glaucoma. These include omega-3 fatty acids, lutein and zeaxanthin, vitamin C, and magnesium.
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel as well as in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These healthy fats have been shown to help protect against dry eye syndrome and reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are two important antioxidants that are found in dark leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens. They help to filter out harmful blue light and protect the eyes from damage. Vitamin C is another powerful antioxidant that can be found in citrus fruits, tomatoes, bell peppers, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. It helps to boost collagen production and fight free radical damage.
Magnesium is an essential mineral that helps to maintain healthy blood pressure levels. It can be found in leafy green vegetables like spinach, Swiss chard, beet greens, turnip greens, and kale as well as in nuts and seeds such as pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, flaxseeds, almonds, cas
Early Detection & Treatments
If you’ve been diagnosed with glaucoma, it’s important to catch the disease early and begin treatment as soon as possible. In the early stages of glaucoma, you may not notice any vision changes. That’s why it’s important to have regular comprehensive eye exams, so your doctor can detect the disease in its early stages and begin treatment right away. Early detection and treatment of glaucoma can help stop the progression of the disease and preserve your vision.
Avoiding Certain Medications and Activities
Be sure to avoid any medications that can raise the pressure in your eye, such as steroids or beta blockers. If you’re not sure if the medication you’re taking is safe, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
You should also avoid activities that put a strain on your eyes, such as reading in low light or rubbing your eyes. And be careful with contact lenses—always clean them properly and don’t wear them for longer than recommended.
Reduce Stress Through Exercise and Relaxation Techniques
Exercise and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress, which can help stop the progression of glaucoma. Physical activity helps pump fluid out of the eye, reducing intraocular pressure. Relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation can help reduce stress levels, which can in turn help reduce pressure on the optic nerve.
Quitting Smoking and
It is never too late to improve your health by quitting smoking. If you smoke, you can significantly reduce your risk of glaucoma and other eye diseases by quitting. Here are some tips to help you quit smoking:
1. Set a quit date and plan ahead for possible challenges.
2. Talk to your doctor about medications that can help with withdrawal symptoms.
3. Remove cigarettes and other tobacco products from your home and workplace.
4. Avoid places where people smoke.
5. Stay positive and focused on your goal of quitting.
Wear Protective Eyewear
Eyewear can help protect your eyes from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays and other environmental factors that can contribute to the development of glaucoma.
Wearing sunglasses or a hat with a brim that shades your eyes when you are outdoors can help reduce your exposure to UV rays. It is also important to wear eye protection when participating in activities that could put your eyes at risk for injury, such as contact sports or using power tools.
Manage Diabetes and Hypertension
If you have diabetes or hypertension, you’re at increased risk for glaucoma. That’s because these conditions can damage the tiny blood vessels in your eyes, causing them to leak fluid or become blocked.
The good news is that you can help prevent or delay the progression of glaucoma by managing your diabetes and hypertension. Here are some tips:
• Control your blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes, it’s important to keep your blood sugar levels under control. High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in your eyes, increasing your risk for glaucoma.
• Take your medications as prescribed: If you have hypertension, it’s important to take your medications as prescribed and to monitor your blood pressure regularly. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss.
• Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help control diabetes and hypertension and promote overall eye health. Foods that are rich in antioxidants, such as leafy green vegetables and fruits, may help protect against glaucoma.
Avoid head-down positions
One of the best things you can do to stop the progression of glaucoma is to avoid head-down positions. This includes activities such as watching television, working on the computer, reading, and even sleeping.
When our heads are in a downward position, the pressure in our eyes increases. This can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss. So it’s important to take breaks from these activities throughout the day and elevate your head when possible.
FAQs
Glaucoma is an eye condition that damages the optic nerve and can lead to blindness. It usually occurs when the pressure inside the eye becomes too high. This may be due to a build-up of fluid in the eye, or it may be caused by other factors such as injury, certain medications, or inherited conditions.
Glaucoma is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam that includes a thorough evaluation of the health of the optic nerve and a measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP). Your doctor may also use other diagnostic tools such as visual field testing or optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Anyone can develop glaucoma, but certain groups of people are at greater risk than others. This includes those over age 60, African Americans, Latinos, Asians, Native Americans, people with a family history of glaucoma, and those with certain medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
Glaucoma cannot be cured, but it can be controlled with early diagnosis and treatment. Treatment options include prescription eye drops, oral medications, laser surgery, and traditional surgery. The goal of treatment is to lower IOP and prevent further damage to the optic nerve.